Hepatitis A (family Picornaviridae, genus Hepatovirus) is highly contagious and usually transmitted via the fecal-oral route, either via person-to-person contact or via contaminated food or water. More than 80% of all adults infected with Hepatitis A display clinical symptoms, whereas the majority of Hepatitis A infected children do not have clinical symptoms.
Clinical symptoms of a Hepatitis A infection may include, fatigue, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain or discomfort, clay-colored bowel movements, loss of appetite, low-grade fever, dark urine, joint pain, yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice). The average incubation period for Hepatitis A infection is 28 days (range 15-50 days post exposure), and as a result, determining the source of hepatitis A infections is challenging.
There are safe and effective vaccines available against Hepatitis A.
Known host species
Samples used for detection of Hepatitis A viruses
Genome
The hepatitis A virus genome consists of a positive strand ssRNA of approximately 7.500 nucleotides. It contains a single ORF that is flanked by 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions (UTR). The 5′ UTR contains the most conserved region of the hepatitis A genome and a internal ribosome entry site (IRES). The ORF encodes a polyprotein that is organized into three functional regions (P1, P2, and P3). P1 is further cleaved to yield the capsid proteins, VP1 to VP4, whereas P2 and P3 encode nonstructural proteins.
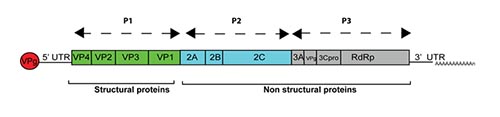
Figure 3. Hepatitis A genome
Nomenclature
There are 6 Hepatitis A genotypes (I to VI), of which, genotypes I, II and III comprise human isolates and genotypes IV, V, and VI comprise simian isolates. Genotypes I to III are further subdivided in two distinct groups (A and B).
Compare reference set
Last update: July 2015
This is a list of all available genotypes of HAV, with one representative per genotype.
For all of the human genotypes, complete genomes have been sequenced. The two incomplete genomes are of simian origin.
As the inter genotype level of variation is in the order of 20% on the nucleotide level, in NGS analysis, a better Blast or mapping result will be obtained when using a representative per genotype instead of the only HAV sequence in the NCBI reference genome database : NC_001489
All genotypes are also available in an automated typing tool. This tool can be used to type individual sequences and is not yet suitable for the analysis of NGS results (http://www.rivm.nl/mpf/hav/typingtool) .